In this class,
Fiorenzo Omenetto and
Benedetto Marelli from SilkLab at Tufts University, described how we can use naturally derived materials for making and building. The guiding principle is to reinvent structural biopolymers into high-technological materials through basic principles of materials science, advanced fabrication and ingenuity. The class will be focused on silk and keratin, materials with thousands of years of history and that now can be engineered to serve at the interface between the biotic and abiotic world. The natural origin of biopolymers also allows for the engineering of materials with remarkably low-energy processing and little environmental impact. By discussing biopolymer regeneration, self-assembly and advanced fabrication we will not only explore a material platform technology at the interface between innovation and sustainability but also introduce a biomaterials based approach that can operate between growing anything and making anything.

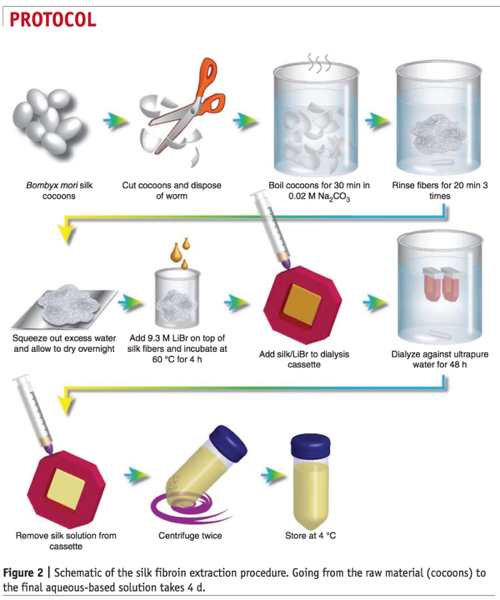
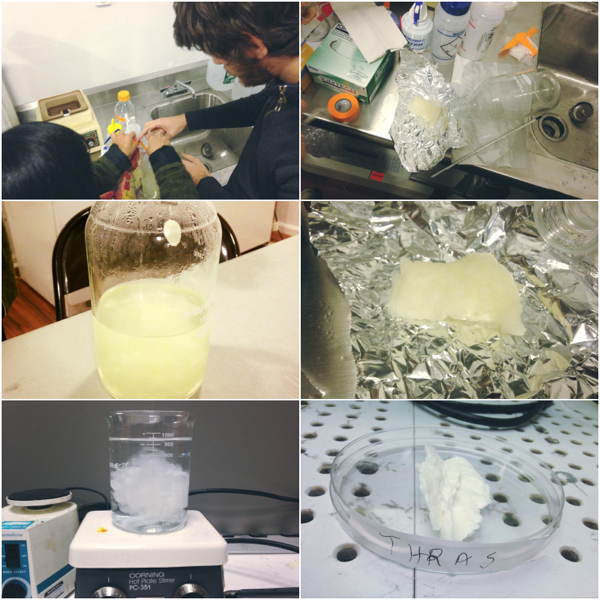
Regenerate silk fibron into an aqueous suspension
Refer to Step 1-23 in Rockwood et al. Nature Protocols, 6, 1612–1631 (2011):
Chopping up caccoons
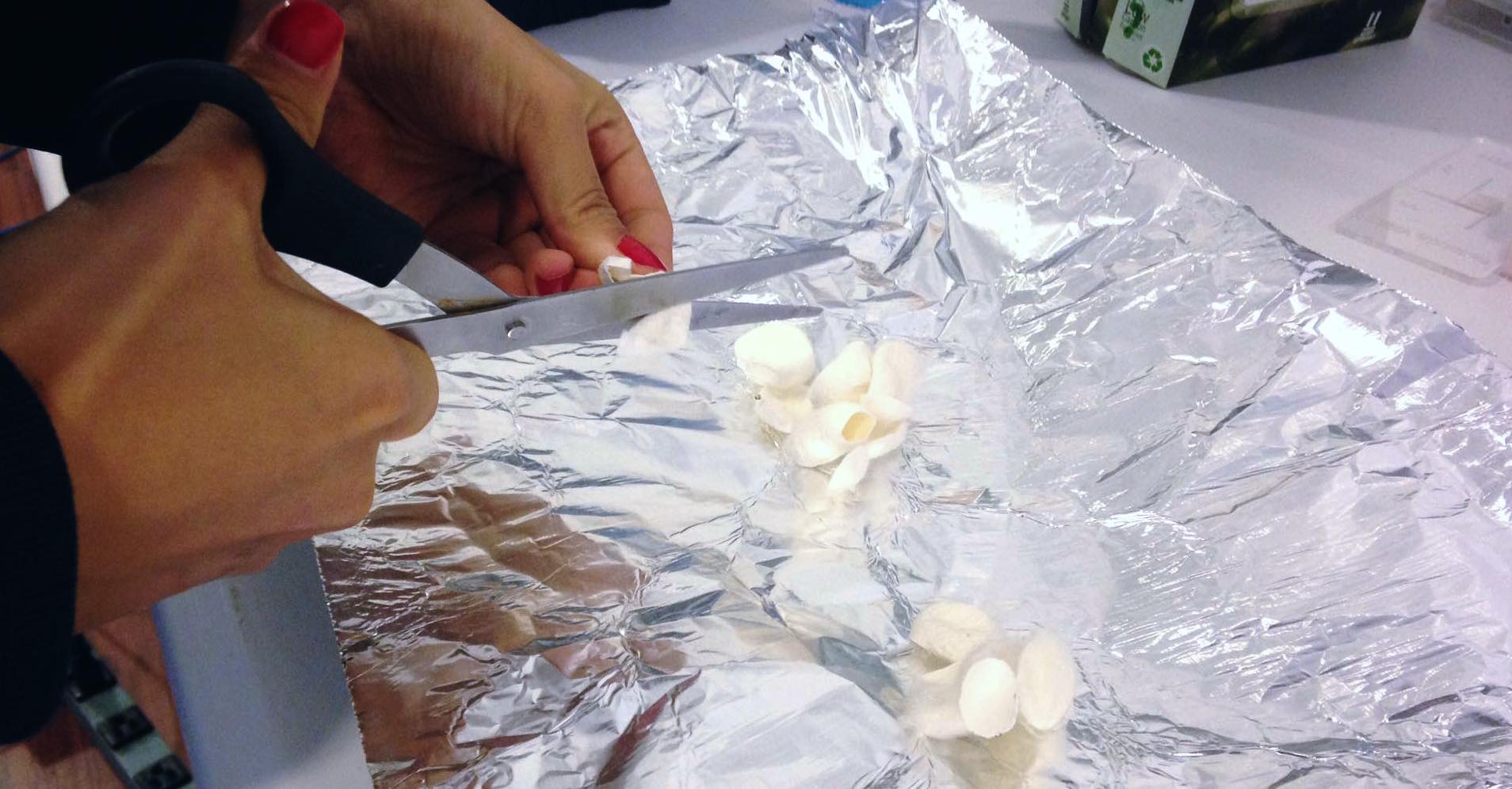

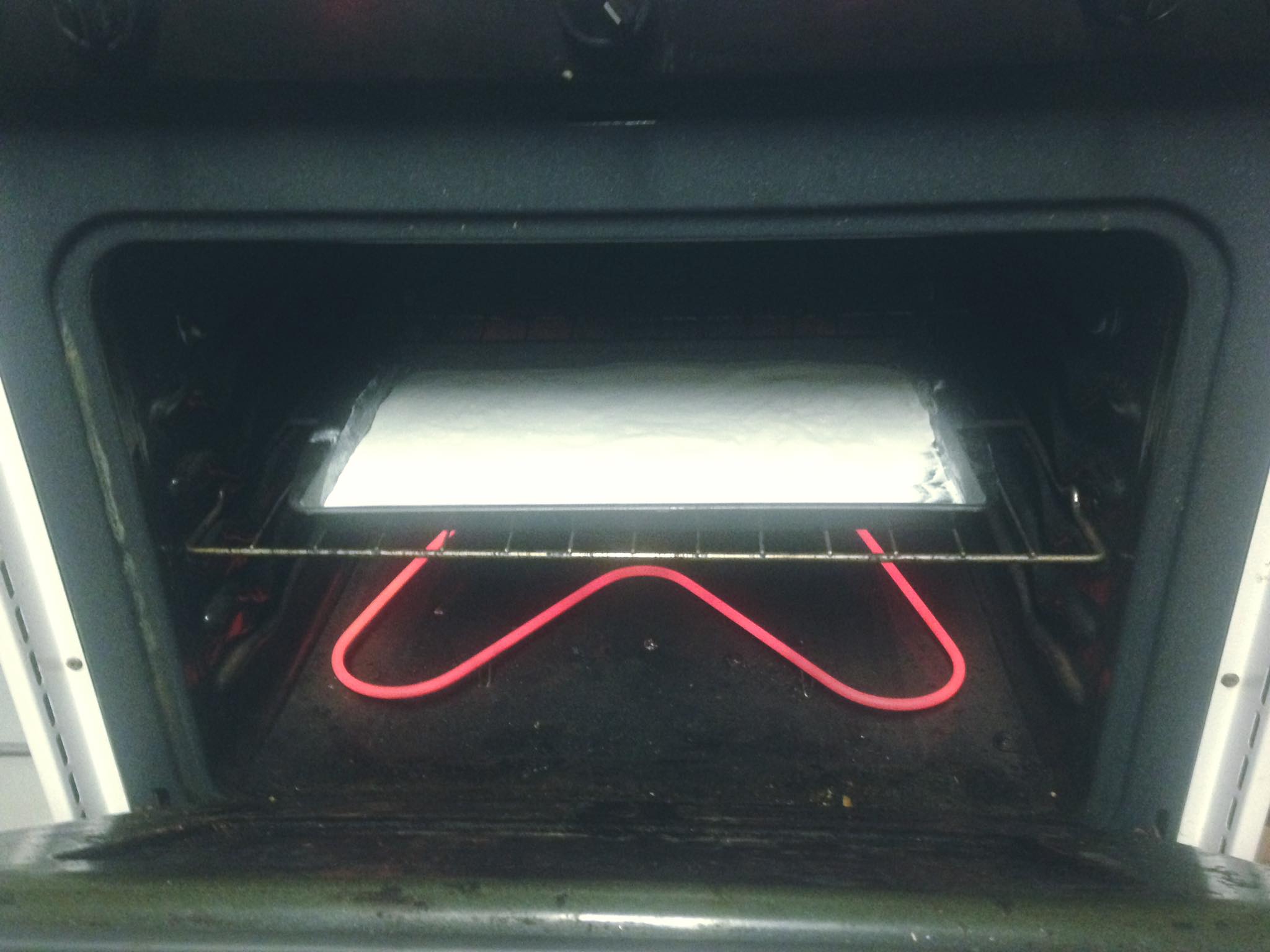
Bake Sodium Bicarbonate (baking soda) @400F to create Sodium Carbonate (washing soda)



Degumming the silk fibroin
Boil caccoons for 30mins in Sodium Carbonate & 1L ultrapure water
Rinse in ultrapure water for 20mins for 3X using a magnetic stir plate

Lithium Bromide Reaction
Put the reaction on ice because it is highly exothermic.
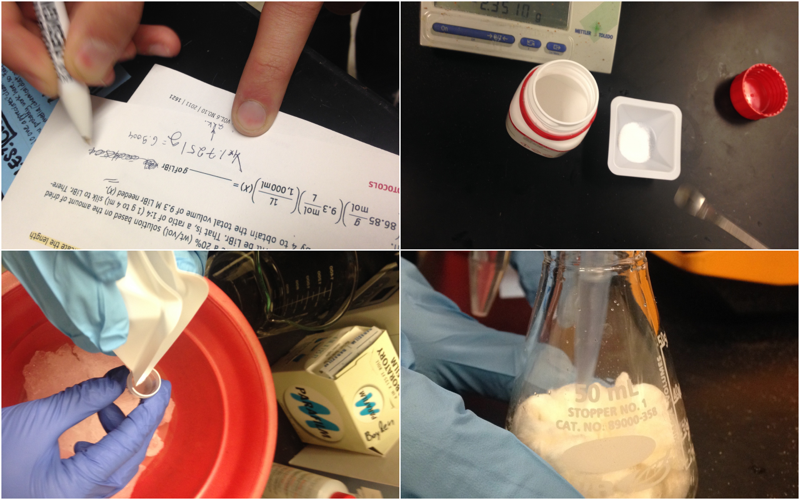
Dissolve silk in LiBr in incubation
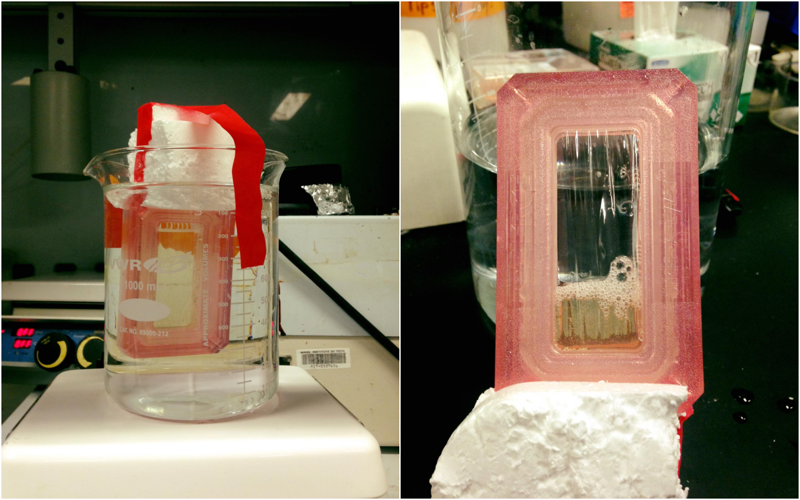
Let LiBr dissolve silk in incubation for 4 hours. Then add silk/LiBr to dialysis cassette.
Note: Pour the silk solution into the top of syringe rather than suck it up to reduce shear.
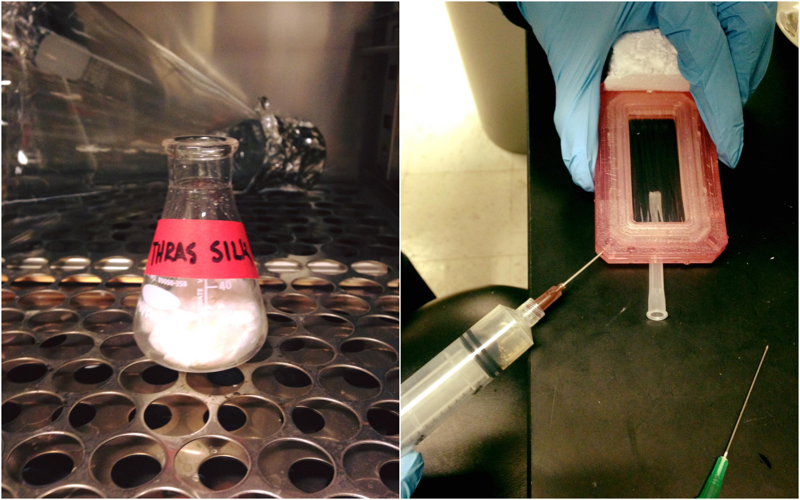

Dialyze against ultrapure water for 48hrs
Then remove silk from cassette.
Note: It is much easier to poke a hole in the cassette then pour into the storage tube rather than trying to suck it out with a syringe.
Fabricate an edible, implantable, biodegradable diffraction grating through soft lithography
Refer to Step 25H in Rockwood et al. Nature Protocols, 6, 1612–1631 (2011)
Biomanufacturing in 3D
Using the silk suspension obtained in Assignment #1 in combination with a XYZ dispensing system for the 3D printing of silk fibroin










![How to grow [almost] anything class Viirj Kan](img/logo.png)