About
I'm currently a senior research scientist at Google, working on foundational models, Bard, and more.
I did my PhD at MIT, where I was advised by Deb Roy in the Media Lab and Jacob Andreas in CSAIL. During my PhD, I spent time at Facebook AI Research with Jason Weston and Stephen Roller, and Google Brain with Peter J. Liu. Before that, I spent one year as a data scientist at Facebook, working on moderation and human-AI interaction. I graduated from UC Berkeley, where I did some research on topological data analysis, bioinformatics, and biomedical imaging.
I work on both capabilities and safety/alignment AI research. I often use real-world applications to motivate advances in methods and understanding of how neural networks work. My ultimate goal is to aid human-AI collaboration at the individual and societal level. My work has sometimes intersected with computational social science, human-AI interaction, and cognitive science.
Latest News
- May 2023: PaLM 2 Technical Report is out.
- May 2023: Paper "Language models trained on media diets can predict public opinion" is cited in US Congressional hearing on AI. Timestamped video and Preprint.
- Spring 2023 and Google I/O: Bard, Bard coding, DuetAI, AI-powered Colab, Search CodeTips are launched.
- May 2022: I joined (Google) X, the Moonshot Factory.
- Oct 2021: Paper on "Evolving Evocative 2D Views of Generated 3D Objects" accepted to NeurIPS creativity and design workshop. Link.
- Sept 2021: Co-leading session on "Designing New Datasets for Social Reasoning & Theory of Mind" in MIT Meaning Representation workshop. Joint program across computer science, linguistics, brain and cognitive science departments. Pre-workshop notes and slides.
- July 2021: Spatial and logical reasoning task accepted to BIG-bench, a benchmark for probing capabilities of large language models. Task and discussion. Task repeatedly highlighted in later scaling papers as difficult task.
Research Interests
Most recently, I've been focused on alignment, learning from human feedback, code LLMs, and planning (tool use, adaptive computation, memory).
*** The following was written in 2021. ***
With the goal of making machine learning more capable, flexible, and deployable, I have experience and interest in:
- Generative sequential models: summarization, dialogue generation, language-guided sketch generation, text style transfer, text simplification, speech synthesis
- Adapatability: compositional models, continual learning,
- Social reasoning and theory of mind: personas, beliefs, pragmatics
- Robustness and human-AI interaction: uncertainty estimation, quality of explanations, experimental design
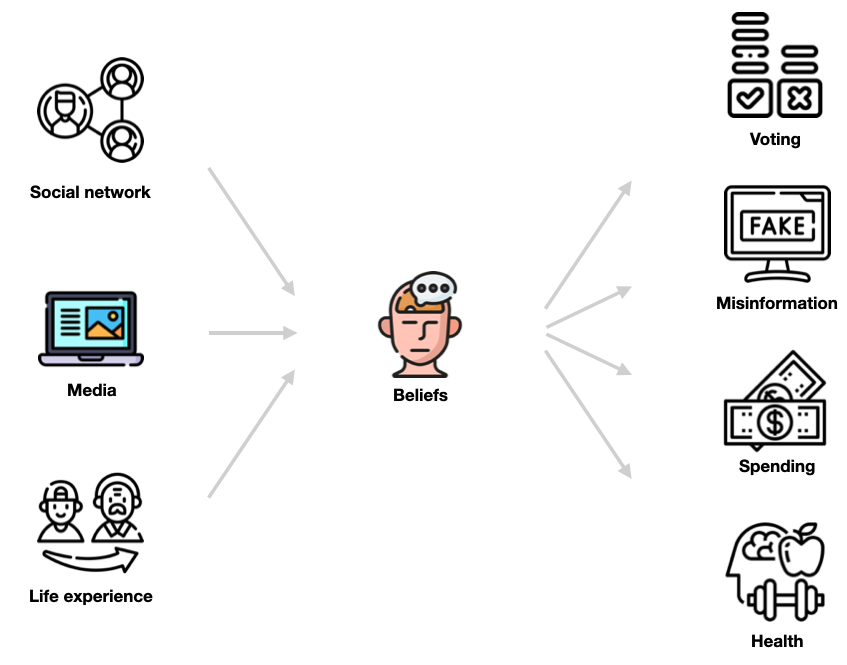
My work is sometimes motivated by the way humans communicate, such as the use of stories and pragmatic implicature, the nature of mass media, social influences on belief formation, and cognitive biases broadly. I started my undergrad as a bioengineering major, and my first stints in research were related to biomedical imaging and protein structure prediction — I remain greatly interested in the potential for machine learning to advance these fields. Finally, I sometimes explore the use of computational tools for art and creative purposes.
Projects
As of Fall 2021, some of my active projects were centered around:
- reasoning steps in large language models
- the effect of model explanations in human collaboration and certification
I believe PhD students and the research community can benefit from more transparency into the non-linear path of research (both in individual projects and in career trajectories), and discussion of negative results. I'm a fan of efforts such as I Can't Believe It's Not Better ⤷, negative results in NLP ⤷, and ML retrospectives ⤷. In that spirit, some smaller, exploratory, incomplete, or negative-results projects I've worked on during my PhD include: (1) hierarichal natural language plans to improve generative models, applied to SketchRNN, (2) disparate impact on minority communities of classifiers that distinguish between human-written and machine-generated text, (3) detecting the provenance of toxic generations in language models, (4) incorporating symbolic rules in neural text simplification, (5) controllable speech synthesis to toggle between natural and tutoring speaking modes, and (6) semi-supervised satellite image segmentation for resource allocation. Several of these projects are described in more detail below.
Media is important in shaping people’s beliefs and behaviors, but (a) traditional surveys for measuring public opinion are expensive, and (b) the tools for measuring media effects are limited. We develop a new approach to simultaneously solve these issues, based on probing language models. We validate our approach against ground-truth surveys in COVID-19 and other settings. More results and paper to come.
Abstractive summarization models have typically required large, paired datasets. However, collecting these datasets is expensive, and existing datasets are typically news-related, which limits the transferrability of trained models to different domains. We consider the setting where there are only documents, and introduce the first end-to-end model for unsupervised, multi-document, abstractive summarization. During training, the summary is a discrete, latent variable that we optimize using the Gumbel-softmax trick. Our model is at least as good compared to extractive baselines when tested on several review datasets.
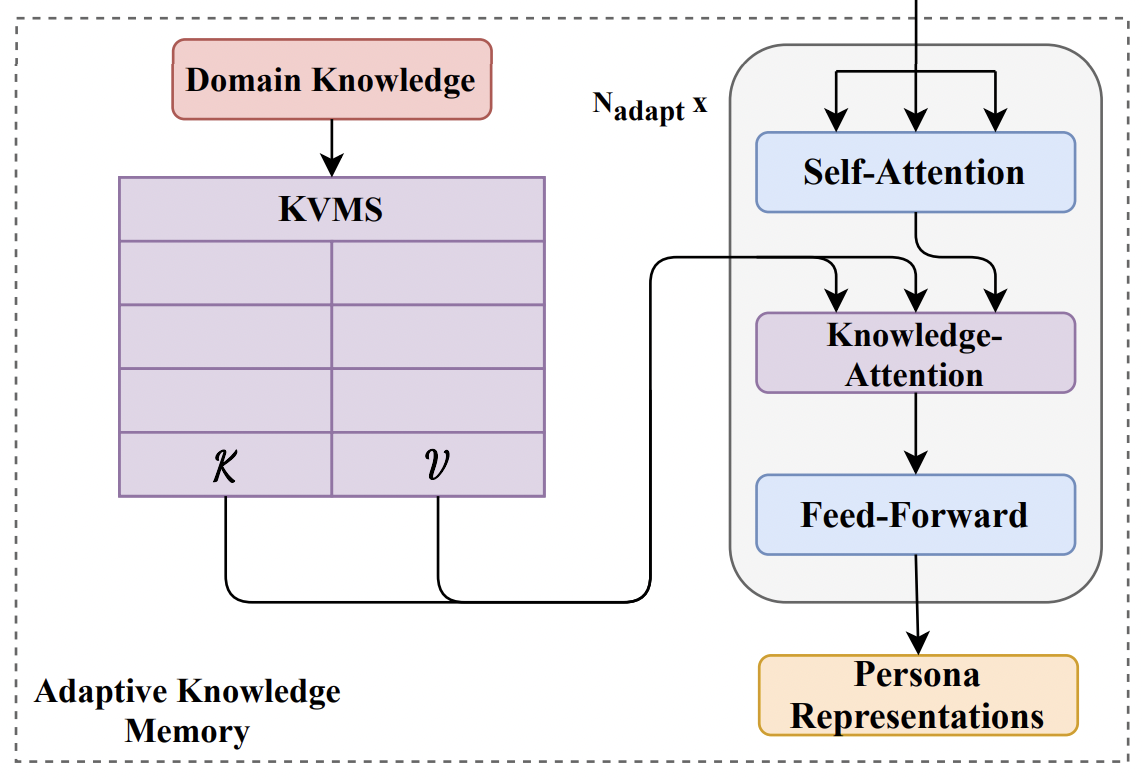
The ability to infer personas is useful in tasks ranging from personalized dialogue generation to computational narrative analysis. In our first work, "Learning Personas from Dialogue with Attentive Memory Networks", we introduce a persona prediction task where character tropes are paired with dialogues. We find that the use of an external "knowledge store" memory module, initialized with descriptions of character tropes, outperforms existing attention and read-write memory models. In a second, follow-up work -- DAPPER -- we extend the use of a knowledge-store memory and find that it improves performance across multiple persona domains, and is useful in downstream tasks like hate-speech detection.
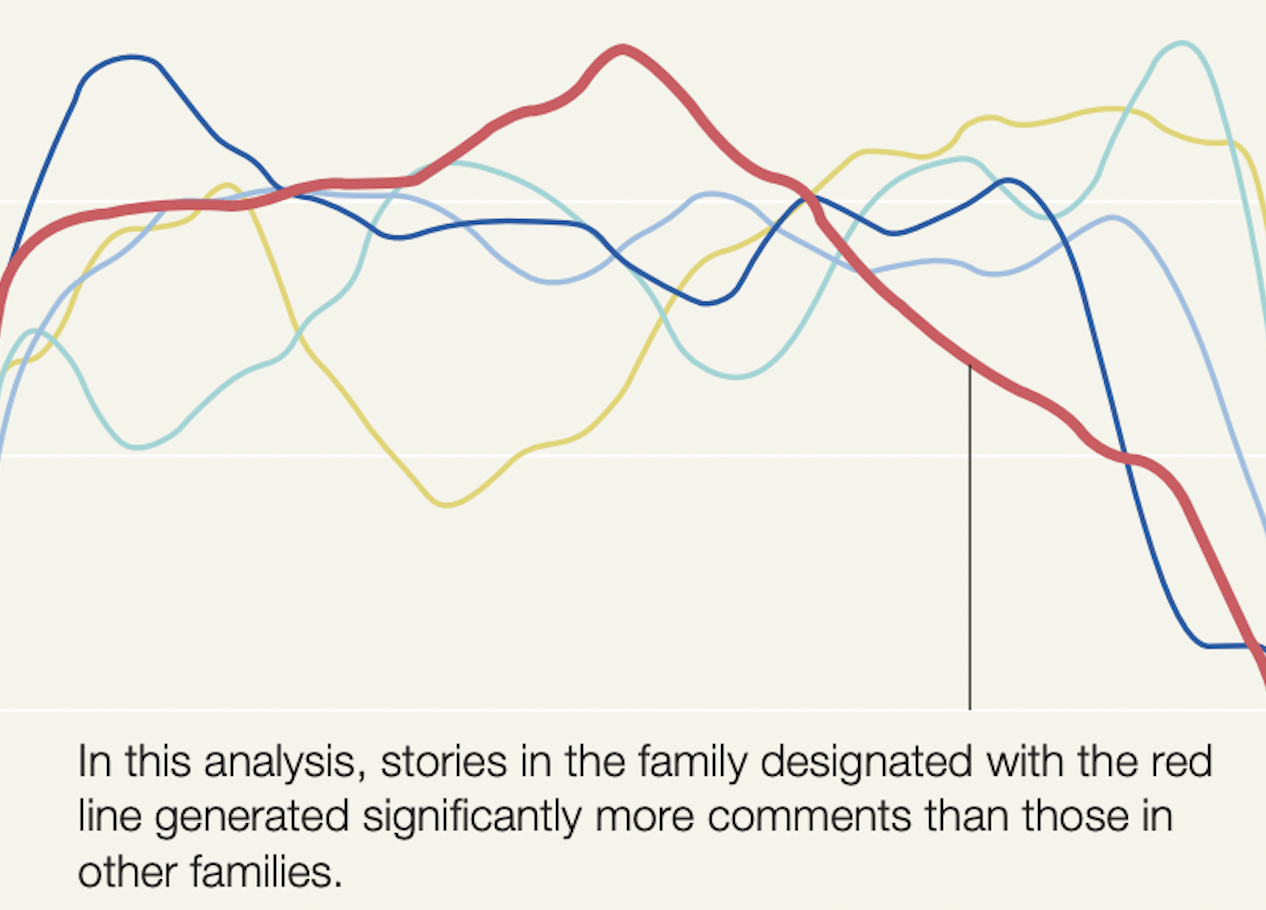
Storytellers and narrative theories have long discussed the importance of the "emotional arc" in determining whether a story resonates with its audience. Concurrent work looked at extracting emotional arcs from text-based stories, but we instead create arcs for movies. We develop neural network-based visual and audio models, trained on both new and existing large-scale datasets, to create separate audio/visual arcs. Crowdsourced annotations of 30-second clips, as well as uncertainty measures of the audio-visual predictions, are used to create a combined arc. We then cluster the arcs by introducing a new method based on k-medioids and dynamic time warping, which fixes several shortcomings of previous work. Finally, we show on a corpus of 1400 short web videos that certain clusters of arcs are significant predictors of likes and comments.
Publications
Most recent publications on Google Scholar.
Neural Language Models of Media Consumption can Predict Public Opinion
Eric Chu, Jacob Andreas, Steve Ansolabehere, Deb Roy
In submission to Nature Human Behavior.
PaLM 2: Technical Report
Are Visual Explanations Useful? A Case Study in Model-in-the-loop Prediction
Eric Chu, Deb Roy, Jacob Andreas
Preprint.
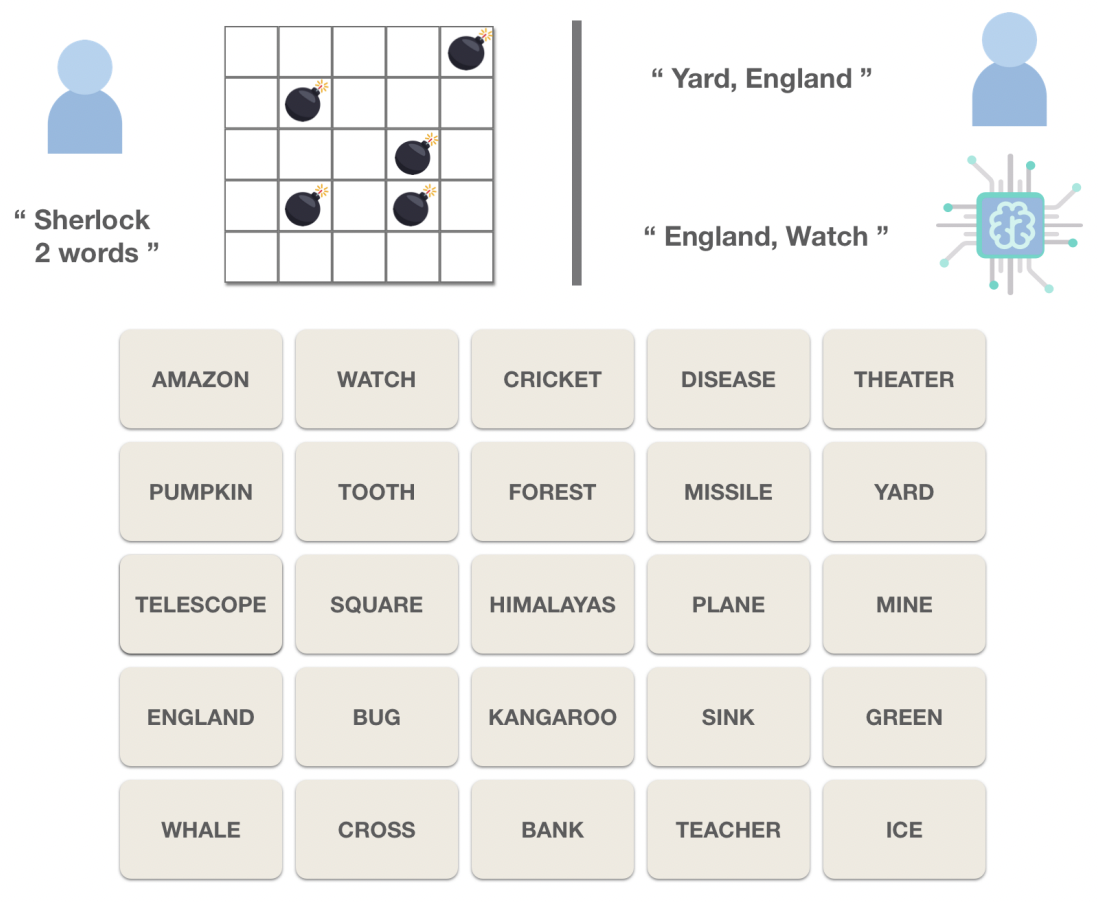
Games for Fairness and Interpretability
Eric Chu‡, Nabeel Gillani‡, Sneha Priscilla Makini
WWW'20: Proceedings of The Web Conference, Workshop on Data Science for Social Good
ICLR'20: International Conference on Learning Representations, Towards Trustworthy ML Workshop
MeanSum : A Neural Model for Unsupervised Multi-Document Abstractive Summarization
Eric Chu‡, Peter J. Liu‡
ICML'19: International Conference on Machine Learning
Learning Personas from Dialogue with Attentive Memory Networks
Eric Chu‡, Prashanth Vijayaraghavan‡, Deb Roy
EMNLP'18: Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing
Audio-visual Sentiment Analysis for Learning Emotional Arcs in Movies
Eric Chu, Deb Roy
ICDM'17: International Conference of Data Mining
ICCV'17: International Conference of Computer Vision, Large Scale Movie Description Challenge
Neural Language Models of Media Consumption can Predict Public Opinion
Eric Chu, Jacob Andreas, Steve Ansolabehere, Deb Roy
In submission to Nature Human Behavior.
PaLM 2: Technical Report
Are Visual Explanations Useful? A Case Study in Model-in-the-loop Prediction
Eric Chu, Deb Roy, Jacob Andreas
Preprint.
Evolving Evocative 2D Views of Generated 3D Objects
Eric Chu
NeurIPS'21: Neural Information Processing Systems, ML for Creativity and Design Workshop
Parents’ Online School Reviews Reflect Several Racial and Socioeconomic Disparities in K–12 Education
Nabeel Gillani, Eric Chu, Doug Beeferman, Rebecca Eynon, Deb Roy
AERA Open '21: American Educational Research Association Journal.
Games for Fairness and Interpretability
Eric Chu‡, Nabeel Gillani‡, Sneha Priscilla Makini
WWW'20: Proceedings of The Web Conference, Workshop on Data Science for Social Good
ICLR'20: International Conference on Learning Representations, Towards Trustworthy ML Workshop
DAPPER: Learning Domain-Adapted Persona Representation Using Pretrained BERT and External Memory
Prashanth Vijayaraghavan, Eric Chu, Deb Roy
AACL'20: Asia-Pacific Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics
MeanSum : A Neural Model for Unsupervised Multi-Document Abstractive Summarization
Eric Chu‡, Peter J. Liu‡
ICML'19: International Conference on Machine Learning
Learning Personas from Dialogue with Attentive Memory Networks
Eric Chu‡, Prashanth Vijayaraghavan‡, Deb Roy
EMNLP'18: Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing
Artistic Influence GAN
Eric Chu
NeurIPS'18: Neural Information Processing Systems, ML for Creativity and Design Workshop
Audio-visual Sentiment Analysis for Learning Emotional Arcs in Movies
Eric Chu, Deb Roy
ICDM'17: International Conference of Data Mining
ICCV'17: International Conference of Computer Vision, Large Scale Movie Description Challenge
Human Atlas: A Tool for Mapping Social Networks
Martin Saveski, Eric Chu, Soroush Vosoughi, Deb Roy
WWW'16: International Conference on the World Wide Web. 2016. (Demo)
CV
Full Resume in PDF.
-
Google 2022 -Senior Research Scientist
-
MIT 2015 - 2021Ph.D. Student
Media Lab, Laboratory for Social Machines -
Facebook AI Research (FAIR) Summer 2019Research Intern
-
Google Brain Summer and Fall 2018Research Intern
-
Facebook 2015Data Scientist
Ads Integrity Team -
UC Berkeley 2010-2014Undergraduate student
Electrical Engineering & Computer Science -
Facebook Summer 2014Data Scientist, Intern
Groups Product -
Knewton Summer 2013Software Engineer, Intern
Ed-tech Platform team -
Oxford University Fall 2013Visiting Student
Mathematics and Bioinformatics