High-precision Brain Function Mapping and Neural Monitoring System Based on ECoG
How to reduce the risk of damaging the epileptic patient's vital function areas during resection of epileptic focus remains a challenge for neurosurgeon. Clinically used electrical cortical stimulation (ECS) method shows limits on accuracy, efficiency and reliability.
In this study, a cortical function mapping method with 3D visualization was implemented by analyzing and projecting the power change of high gamma (HG) oscillation in ECoG on patient's own MRI brain model. The method was tested on epileptic patients with subdural electrodes for three tasks (hand movement, tongue movement and silent reading). The proposed 3D cortical function mapping on the patient's individual brain structure provides direct and accurate reference for resection surgery planning.
Identified as a national initiative by Chinese National Academy of Sciences
Got the grand prize in the 6th "Challenge Cup" Extracurricular Academic Science and Technology Competition for Capital College Students
Got the third prize in the 12th "Challenge Cup" Extracurricular Academic Science and Technology Competition for National College Students

Target - Epilepsy Treatment
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent unprovoked seizures. Although most epileptic seizures can be controlled by antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), there are still approximately 30% of the epilepsy sufferers cannot be cured by AEDs, and surgical operations must always be considered as viable option.
Background
Before the lesion surgery, mapping of the patient’s brain function is needed to define the position of the surgical lesion and the critical functional areas. At present, electrical cortical stimulation (ECS) has been applied as the ‘Golden Standard’ of cortical function mapping. The surgical plan of resection can be made by evaluating the reaction of the patients as well as the phenomena such as the emergence of sensations, motions and language interruption evoked by the ECS in different cortical regions.
However, there are several limitations on electrical stimulation:
1) The duration of a complete stimulation usually lasts for hours, for the stimulation has to be undergone along with the changing and pairing of stimulated electrodes.
2) The intensity of the evoked phenomena are largely depended on the intensity and parameters of the stimulations and on the characteristics of individual cortex.
3) The ECS relies on patient compliance and cooperation that are hardly available in some cases.
4) Inappropriate operation and the lack of experience of the operators usually lead to erroneous “negative mapping”.
5) After-discharge is also a negative point of ECS.
Therefore, in this study, a new cortical function mapping method with 3D visualization was implemented by analyzing and projecting the power change of high gamma (HG) oscillation in ECoG on patient's own MRI brain model.

Block diagram of the system
3D Co-registration Module

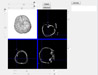
3D Co-registration Results
The registration results can be evaluated by mapping the inner contour of skull on the MRI cerebral cortex model and then measuring whether they are coincide with each other. The registration result is shown above, which has been calibrated by 30 contour points with average error of 2.6mm.
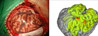
3D Visualization Module

3D Visualization Results
2D Visualization Module / Video & Waveform Playback Module / Neural Monitoring Module
An application example recorded by China Central Television (CCTV)