Situation Fencing: Making Geo-Fencing Personal and Dynamic
Geo-fencing has recently been applied to multiple applications including media recommendation, advertisements, wildlife monitoring, and recreational activities.
However current geo-fencing systems work with static geographical boundaries. Situation Fencing allows for these boundaries to vary automatically based on situations derived by a
combination of global and personal data streams.
This concept has wide reaching implications.
Multimedia data is now created at a macro, public scale as well as individual personal scale.
While distributed multimedia streams (e.g. images, microblogs, and sensor readings) have recently been
combined to understand multiple spatio-temporal phenomena like epidemic spreads, seasonal patterns, and political situations;
personal data (via mobile sensors, quantified-self technologies) are now being used to identify user behavior,
intent, affect, social connections, health, gaze, and interest level in real time.
An effective combination of the two types of data can revolutionize multiple applications ranging from healthcare,
to mobility, to product recommendation, to content delivery. Building systems at this intersection can lead to better orchestrated
media systems that may also improve users' social, emotional and physical well-being.
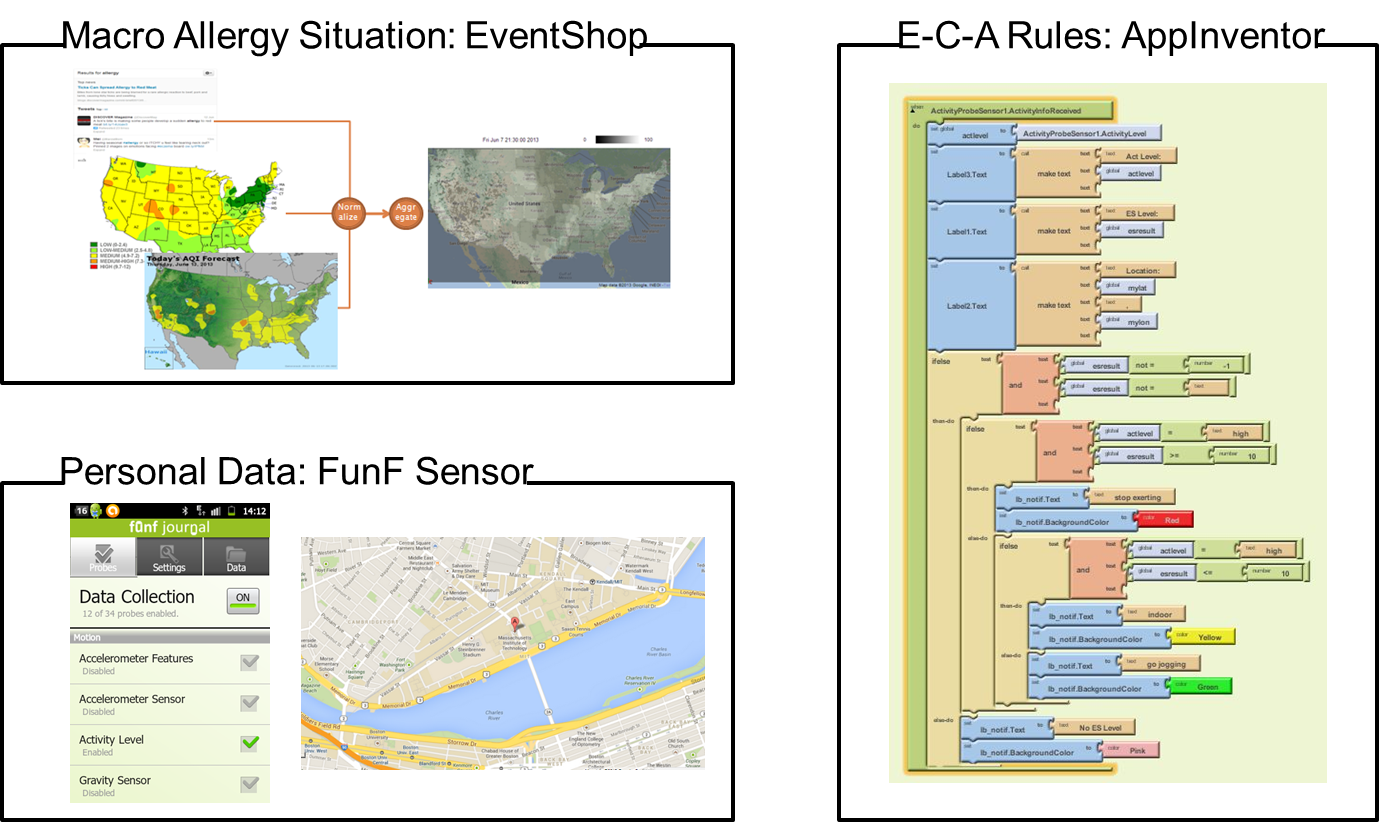
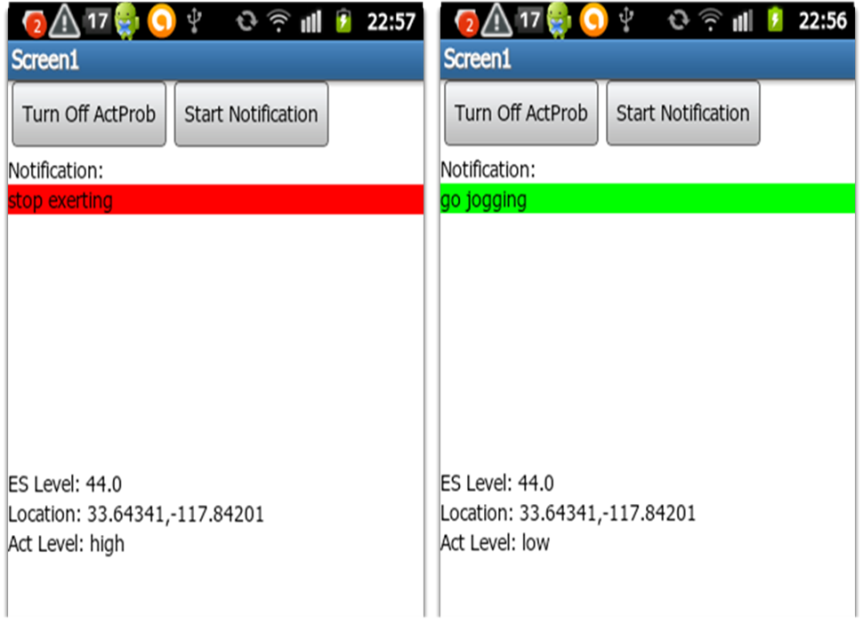
Example 1: Personalized recommendattions to Asthmatic users:
Ccmbining layers of enviromental data (Pollen count, Air Quality, and Allergy reports on Twitter) with Personal data (exertion level) to give personalized recommendations to users.
Relevant Publication:
1). S. Pongpaichet, V. K. Singh, R. Jain and A. Pentland, Situation Fencing: Making Geo-Fencing Personal
and Dynamic, ACM MM: Workshop on Personal Data Meets Distributed Multimedia, 2013 (ACM MM – PDM’13).
We were very happy to see the excitement in the community about similar ideas. Check out our workshop website, where multiple researchers presented their ideas on combining personal and distributed heterogeneous data.